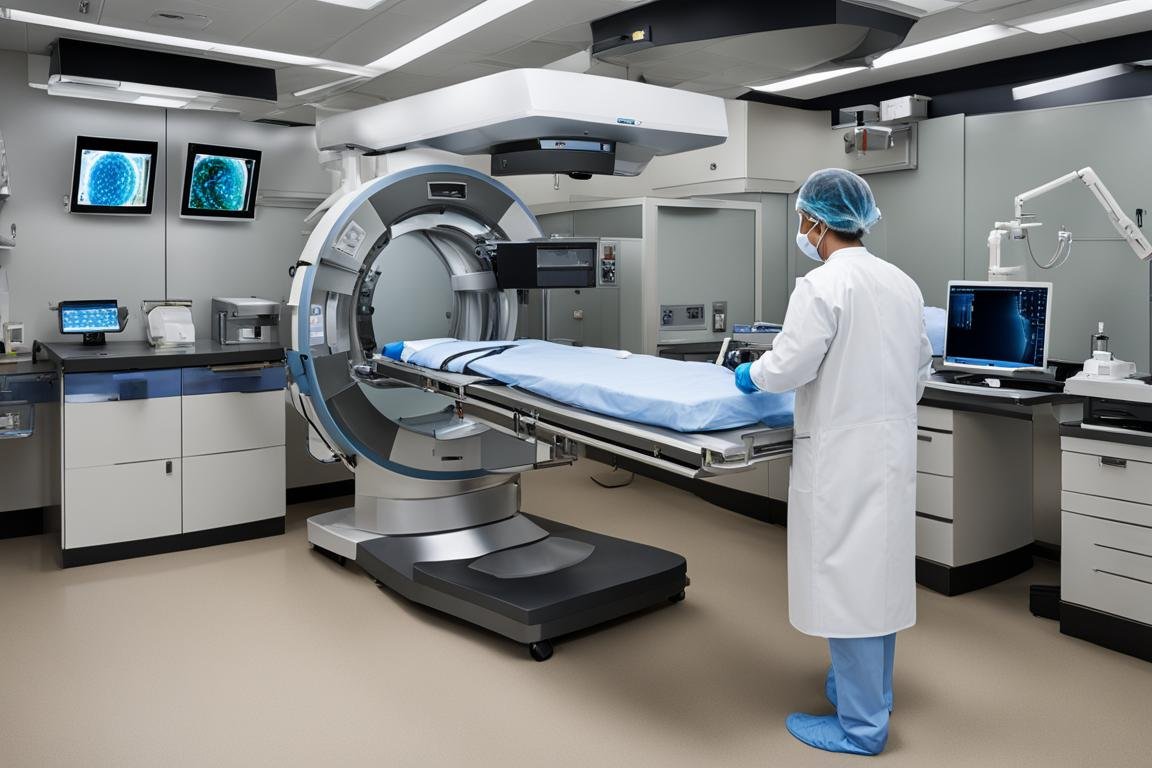
In the field of diagnostic imaging, nuclear medicine technologists play a crucial role in performing nuclear medicine procedures to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions. Using imaging technology and radiopharmaceuticals, these professionals administer radioactive tracers to patients, allowing for the visualization and assessment of organs and tissue functions through nuclear imaging.
Nuclear medicine technologists are trained in radiation safety to ensure the well-being of both themselves and their patients during the use of radioactive materials. Their expertise in medical imaging and radiation safety makes them an indispensable part of the healthcare team.
If you are interested in a career as a nuclear medicine technologist, this guide will provide you with valuable information on the necessary education and certification, career opportunities, salary expectations, and more.
Key Takeaways:
- Nuclear medicine technologists administer radioactive tracers for diagnostic imaging procedures.
- They play a crucial role in maintaining radiation safety for themselves and their patients.
- Career opportunities for nuclear medicine technologists include working in hospitals, medical clinics, and research centers.
- Education requirements typically include an associate or bachelor’s degree in nuclear medicine technology.
- The median annual salary for nuclear medicine technologists is approximately $79,000.
What do Nuclear Medicine Technologists do?
Nuclear medicine technologists play a vital role in the field of diagnostic imaging and patient care. They are responsible for a range of tasks related to the use of radioactive drugs and imaging equipment. Let’s take a closer look at the key responsibilities of nuclear medicine technologists:
- Explaining medical procedures to patients: Nuclear medicine technologists communicate with patients, informing them about the procedures they will undergo and addressing any concerns or questions.
- Preparing and administering radioactive drugs: They are trained in the proper preparation and administration of radiopharmaceuticals, ensuring accurate dosage and delivery.
- Monitoring patients for reactions: During and after the administration of radioactive drugs, nuclear medicine technologists closely monitor patients for any adverse reactions, providing immediate medical attention if necessary.
- Operating imaging equipment: They are skilled in operating sophisticated imaging equipment, such as gamma cameras and PET scanners, to capture images of organs, tissues, and bodily functions.
- Keeping detailed records: Nuclear medicine technologists maintain accurate and comprehensive records of patient procedures, including dosage, imaging results, and other relevant data.
- Following radiation disposal and safety procedures: They adhere to strict protocols for handling and disposing of radioactive materials, ensuring the safety of both patients and medical staff.
Nuclear medicine technologists work with radiopharmaceuticals to monitor tissue and organ functions, detect abnormalities, and assist physicians in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. Through their expertise in imaging technology and radiation safety, they contribute to the accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of patients.
“Nuclear medicine technologists play a crucial role in diagnostic imaging and patient care, utilizing radioactive drugs and advanced imaging equipment to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatment.”
In addition to their regular duties, nuclear medicine technologists are trained to respond to emergencies related to radioactive incidents or nuclear disasters. Their expertise in radiation detection and monitoring allows them to contribute to emergency response efforts, ensuring the safety of individuals affected by such incidents.
Career Opportunities for Nuclear Medicine Technologists
Nuclear medicine technologists have various career opportunities within the field of diagnostic imaging and patient care. These professionals play critical roles in providing accurate diagnoses and effective treatments, working closely with physicians and other healthcare professionals. The following are some of the career paths available to nuclear medicine technologists:
- Certified Nuclear Medicine Technologists – These technologists have received certification in nuclear medicine technology, demonstrating their expertise and commitment to providing quality patient care.
- Isotope Technologists – Isotope technologists specialize in working with radioactive isotopes to perform imaging procedures and assist in the diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions.
- Nuclear Cardiology Technologists – Nuclear cardiology technologists focus on imaging techniques specific to the cardiovascular system, helping to diagnose and monitor heart conditions.
- Nuclear Medical Technologists – Nuclear medical technologists are responsible for administering radioactive drugs and conducting imaging procedures to detect abnormalities and facilitate the diagnosis of medical conditions.
- PET Technologists – PET technologists specialize in positron emission tomography, an advanced imaging technique used to visualize and analyze metabolic processes in the body.
- Registered Nuclear Medicine Technologists – These technologists are registered with professional organizations and have met the necessary requirements to practice nuclear medicine technology.
With these career opportunities, nuclear medicine technologists can explore different areas of specialization and contribute to advancing healthcare through their skills and expertise.

Real-Life Example:
“I began my career as a nuclear medicine technologist and later specialized as a PET technologist. This specialization allowed me to work closely with oncologists and help in the detection and monitoring of various cancers. It’s a rewarding profession that combines technical expertise with the opportunity to make a difference in patients’ lives.”
Career Advancement and Growth
Nuclear medicine technologists can further advance their careers by pursuing additional education and training. This can include obtaining specialty certificates in areas such as PET or other advanced imaging techniques. With experience and additional qualifications, nuclear medicine technologists may also progress into leadership roles, research positions, or educational roles within the field.
| Career Advancement Opportunities | Description |
|---|---|
| Lead Technologist | Responsible for overseeing a team of nuclear medicine technologists and ensuring smooth workflow in a clinical or hospital setting. |
| Research Technologist | Involved in research and development of new imaging techniques and technologies, contributing to advancements in the field of nuclear medicine. |
| Management Role | Opportunity to move into management positions within healthcare organizations, overseeing nuclear medicine departments and operations. |
| Education Role | Teaching and training future nuclear medicine technologists, sharing knowledge and expertise with the next generation of professionals. |
Through continuous learning and career development, nuclear medicine technologists can expand their skillset, increase their earning potential, and make significant contributions to the field of nuclear medicine.
Becoming a Nuclear Medicine Technologist
To become a nuclear medicine technologist, individuals typically need to complete higher education requirements in the field. This can be achieved through earning an associate degree, bachelor’s degree, or certificate program specializing in nuclear medicine technology.
An associate degree in nuclear medicine technology provides a solid foundation of knowledge and skills necessary to begin a career in the field. These programs typically take about two years to complete and include coursework in anatomy, physiology, radiation safety, and nuclear medicine procedures.
A bachelor’s degree in nuclear medicine technology offers a more in-depth education and can provide advanced career opportunities and specialization options. These programs generally take four years to complete and often include hands-on clinical experience, research opportunities, and coursework in nuclear physics, instrumentation, and advanced imaging techniques.
For individuals looking for a shorter time frame to enter the field, certificate programs in nuclear medicine technology are available. These programs usually take about one to two years to complete and focus solely on the core competencies needed to become a nuclear medicine technologist.
After completing the necessary education, certification or licensure is often required by employers to ensure competency and professionalism. These credentials can be obtained by passing a certifying exam administered by organizations such as the Nuclear Medicine Technology Certification Board or the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists.

Career Outlook for Nuclear Medicine Technologists
The field of nuclear medicine technology offers promising career prospects for individuals interested in diagnostic imaging and patient care. With the increasing demand for diagnostic procedures, including nuclear medicine testing, the job growth rate for nuclear medicine technologists is projected to be 8% from 2020 to 2030, according to the Occupational Outlook Handbook published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
One of the factors contributing to the positive career outlook is the growing middle-aged and older adult populations, who require extensive medical imaging and diagnostic services. This population trend fuels the need for skilled nuclear medicine technologists to perform and interpret various nuclear medicine scans and procedures.
“The job growth rate for nuclear medicine technologists is projected to be 8% from 2020 to 2030, according to the Occupational Outlook Handbook.”
Aside from the promising job growth, nuclear medicine technologists also enjoy a competitive median annual salary of approximately $79,000. This compensation reflects the specialized skills and expertise required in the field, as well as the significant impact these professionals have on patient care and diagnostic accuracy.
The career outlook for nuclear medicine technologists is further supported by advancements in technology and research within the healthcare industry. As new imaging techniques and radiopharmaceuticals continue to be developed, the demand for skilled nuclear medicine technologists will continue to grow, ensuring a stable and rewarding career path for individuals entering the field.

Key Points:
- Projected job growth rate of 8% from 2020 to 2030 for nuclear medicine technologists.
- Median annual salary for nuclear medicine technologists is approximately $79,000.
- Increasing demand for diagnostic procedures drives career opportunities in the field.
- Advancements in technology and research support the long-term growth of the nuclear medicine technology industry.
Training and Education Requirements for Nuclear Medicine Technologists
To pursue a career as a nuclear medicine technologist, individuals typically need to complete an associate degree or bachelor’s degree in nuclear medicine technology. Alternatively, some may choose to complete a certificate program specializing in nuclear medicine technology. These educational programs provide the necessary knowledge and skills in diagnostic imaging, radiation safety, and patient care to prepare individuals for careers as nuclear medicine technologists.
Here are the main education paths to becoming a nuclear medicine technologist:
- Associate Degree in Nuclear Medicine Technology: This program typically takes two years to complete and provides a comprehensive foundation in nuclear medicine technology. Students learn about medical imaging techniques, radiation safety, patient care, and the administration of radiopharmaceuticals. Clinical internships are usually included to gain hands-on experience in a healthcare setting.
- Bachelor’s Degree in Nuclear Medicine Technology: This four-year program offers a more in-depth study of nuclear medicine technology. Students acquire advanced knowledge in nuclear medicine procedures, diagnostic imaging, and radiation physics. The curriculum may also cover research methods and healthcare management. Clinical practicum experiences are typically included to develop practical skills.
- Certificate Program in Nuclear Medicine Technology: This option is suitable for individuals who already have a degree or relevant healthcare experience but require specialized training in nuclear medicine technology. Certificate programs are shorter and focus on core topics in nuclear medicine. These programs may be completed in one to two years and provide a condensed curriculum focused on essential skills and knowledge.
Upon completing their education, aspiring nuclear medicine technologists often pursue certification or licensure to enhance their job prospects and demonstrate their competence in the field. Certification can be obtained through organizations such as the Nuclear Medicine Technology Certification Board (NMTCB) or the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT). These certifications validate the technologist’s knowledge and skills in nuclear medicine technology.

Aspiring nuclear medicine technologists can choose the educational path that best suits their career goals and interests. Whether pursuing an associate degree, bachelor’s degree, or certificate program, these educational programs provide a solid foundation for a successful career in nuclear medicine technology.
Specializations in Nuclear Medicine Technology
Nuclear medicine technologists have the opportunity to specialize in various areas within the field. By pursuing specialized certification and training, these professionals can enhance their skills and expertise in specific applications of nuclear medicine technology.
One specialization option is positron emission tomography (PET), which involves advanced imaging techniques using radioactive tracers to detect and monitor diseases such as cancer, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular conditions. PET scans provide detailed three-dimensional images that help physicians make accurate diagnoses and track the effectiveness of treatments.
Another specialization is nuclear cardiology, which focuses on cardiovascular imaging. Nuclear medicine technologists specializing in this area use radiopharmaceuticals to assess the functioning of the heart and diagnose conditions such as coronary artery disease, myocardial infarctions, and heart failure. These specialized imaging techniques help guide treatment plans for cardiovascular patients.
In addition to PET and cardiovascular imaging, nuclear medicine technologists can also specialize in three-dimensional imaging. This specialization involves utilizing advanced software and imaging techniques to reconstruct three-dimensional images of organs and tissues, providing detailed anatomical information to assist in diagnosis and treatment planning.
These specializations offer nuclear medicine technologists the opportunity to expand their career options and develop expertise in specific areas of nuclear medicine technology. By focusing their skills on specialized applications, they can contribute to more accurate diagnoses and improved patient outcomes.

“Specializing in specific areas of nuclear medicine technology allows technologists to provide more accurate diagnoses and targeted treatments, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.” – Dr. Emily Johnson, Chief Nuclear Medicine Technologist at XYZ Hospital.
Work Environment for Nuclear Medicine Technologists
Nuclear medicine technologists work in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, medical clinics, imaging clinics, diagnostic labs, and research centers. These professionals play a crucial role in the field of nuclear medicine, assisting physicians in diagnosing and treating patients through the use of radioactive drugs and imaging technology.
Within hospitals, nuclear medicine technologists are typically employed in the radiology department or nuclear medicine department. They collaborate closely with physicians, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure accurate imaging and effective patient care. In medical clinics and imaging clinics, technologists often work alongside radiologists and other specialized technicians to conduct diagnostic scans and administer radiopharmaceuticals for imaging purposes.
Diagnostic labs and research centers also employ nuclear medicine technologists who contribute to scientific investigations and clinical trials involving nuclear medicine procedures. These environments provide opportunities for technologists to participate in cutting-edge research and contribute to advancements in medical imaging and nuclear medicine treatments.
The work environment for nuclear medicine technologists is typically safe and requires adherence to stringent radiation safety protocols. Technologists are responsible for maintaining the safety of both themselves and their patients, ensuring that proper precautions are taken to minimize radiation exposure. This includes using shielding devices, monitoring radiation levels, and disposing of radioactive materials in accordance with established guidelines.
Technologists generally work a standard 40-hour week, which may include evening or weekend shifts depending on the specific healthcare facility. Some technologists may also have on-call responsibilities, especially in larger hospitals or facilities that provide 24/7 medical services.
“The work environment for nuclear medicine technologists is diverse, encompassing a range of healthcare settings where they contribute to the diagnosis and treatment of patients through the use of radioactive drugs and advanced imaging technology.”

Overall, the work environment for nuclear medicine technologists offers a rewarding and fulfilling experience, allowing professionals to make a significant impact on patient care and contribute to advancements in medical imaging and nuclear medicine.
Additional Training and Career Advancement Opportunities
Nuclear medicine technologists have the opportunity to further their careers through additional training and gain valuable experience in the field. This can open doors to various advancement opportunities and specialized roles within nuclear medicine technology.
Lead Technologist
With advanced training and expertise, nuclear medicine technologists can strive for leadership positions as lead technologists. In this role, they oversee the day-to-day operations of the nuclear medicine department, supervise staff, and ensure quality control and radiation safety compliance.
Research Technologist
For those interested in the research aspect of nuclear medicine, becoming a research technologist is a viable path. Research technologists work on clinical trials, collaborate with scientists and physicians, and contribute to the development of new imaging techniques and radiopharmaceuticals.
Management Roles
Nuclear medicine technologists with excellent leadership and organizational skills can move into management roles within healthcare organizations. These roles involve overseeing multiple departments or imaging facilities, managing budgets, and implementing strategic initiatives to improve patient care and operational efficiency.
Education Roles
If you have a passion for teaching and mentoring, pursuing an education role within the field of nuclear medicine technology can be fulfilling. As an educator, you can train and guide aspiring nuclear medicine technologists, develop curriculum, and contribute to the advancement of the profession.
Specialty Certificates
Earning specialty certificates in specific areas of nuclear medicine technology can enhance career prospects and demonstrate expertise in specialized imaging techniques. Some popular specialty certificates include positron emission tomography (PET) and other advanced imaging modalities.
“Continuing education and specialization are key factors in advancing as a nuclear medicine technologist. These opportunities allow technologists to develop their skills, take on leadership roles, and contribute to cutting-edge research and patient care.” – Dr. Sarah Roberts, Chief Nuclear Medicine Technologist at XYZ Hospital
Mayo Clinic Nuclear Medicine Technologist Program
Mayo Clinic offers a one-year Nuclear Medicine Technology Program in Rochester, Minnesota, to prepare students for careers as nuclear medicine technologists. This comprehensive program provides rigorous training in diagnostic imaging technology and radiation safety, equipping students with the knowledge and skills necessary for success in the field.
Throughout the program, students will gain theoretical knowledge and practical experience in performing nuclear medicine procedures, operating imaging equipment, and administering radioactive tracers. They will also learn to analyze images and assist physicians in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
The Mayo Clinic Nuclear Medicine Technologist Program places a strong emphasis on hands-on training, allowing students to work directly with experienced professionals in a clinical setting. This practical experience prepares graduates to confidently enter the workforce and provide high-quality patient care.
Career Preparation
By attending the Mayo Clinic Nuclear Medicine Technologist Program, students will receive top-notch education that prepares them for a successful career in the field. The program’s curriculum covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Radiation safety protocols and procedures
- Diagnostic imaging techniques and technologies
- Medical ethics and patient care
- Quality control and assurance
- Research methods and data analysis
In addition to the comprehensive coursework, students will have the opportunity to gain practical experience through clinical rotations at Mayo Clinic’s world-renowned medical facilities. These rotations provide invaluable hands-on training, allowing students to apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios and further develop their skills.
Upon completion of the program, graduates will be well-prepared to pursue careers as nuclear medicine technologists in various healthcare settings, including:
- Hospitals
- Medical clinics
- Imaging centers
- Research laboratories
The Mayo Clinic Nuclear Medicine Technologist Program is highly respected in the industry and offers graduates a competitive edge in the job market. The program’s strong reputation, combined with Mayo Clinic’s prestigious name, provides graduates with excellent career prospects and opportunities for advancement.
For individuals interested in pursuing a rewarding career as a nuclear medicine technologist, the Mayo Clinic Nuclear Medicine Technologist Program in Rochester, Minnesota, offers comprehensive education and practical training, setting students up for success in this rapidly growing field.

Section 11: Similar Careers in the Medical Field
Similar Careers in the Medical Field
Individuals interested in the medical field but not specifically in nuclear medicine technology may consider similar careers. These include nuclear technicians, radiation therapists, medical and clinical laboratory technologists and technicians, biological technicians, and exercise physiologists. These careers offer opportunities to work in diagnostic imaging, radiation therapy, laboratory analysis, and other healthcare-related fields.
Nuclear Technicians
Nuclear technicians play a vital role in the operation and maintenance of nuclear power plants and other nuclear facilities. They work with nuclear engineers and scientists to monitor radiation levels, perform quality control tests, and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Nuclear technicians require specialized training and certification to work in this field.
Radiation Therapists
Radiation therapists collaborate with oncologists and other healthcare professionals to administer radiation treatments to patients with cancer and other diseases. They operate radiation therapy equipment, monitor patient progress, and ensure accurate treatment delivery. Radiation therapists require a bachelor’s degree and certification in radiation therapy.
Medical and Clinical Laboratory Technologists and Technicians
Medical and clinical laboratory technologists and technicians perform laboratory tests and analyses on patient samples to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. They work with sophisticated laboratory equipment and instruments, interpret test results, and collaborate with healthcare professionals. These professionals typically hold a bachelor’s degree and may be required to obtain certification or licensure.
Biological Technicians
Biological technicians assist scientists and researchers in conducting experiments and analyzing biological samples. They may be involved in activities such as collecting and preparing samples, operating laboratory equipment, recording data, and maintaining laboratory inventory. Biological technicians typically have an associate degree or bachelor’s degree in biology or a related field.
Exercise Physiologists
Exercise physiologists work with individuals to develop and implement exercise programs that promote health, fitness, and rehabilitation. They assess patients’ fitness levels, monitor vital signs during exercise, and provide guidance on exercise techniques and nutrition. Exercise physiologists typically hold a bachelor’s degree in exercise physiology or a related field and may need certification.

| Career | Education Requirement | Certification/Licensure |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear Technicians | Associate degree or vocational training | Certification may be required |
| Radiation Therapists | Bachelor’s degree in radiation therapy or related field | Certification/licensure required |
| Medical and Clinical Laboratory Technologists and Technicians | Bachelor’s degree in medical laboratory science or related field | Certification/licensure may be required |
| Biological Technicians | Associate or bachelor’s degree in biology or related field | Certification/licensure not typically required |
| Exercise Physiologists | Bachelor’s degree in exercise physiology or related field | Certification may be required depending on employment setting |
Conclusion
In conclusion, a career as a nuclear medicine technologist offers a rewarding path in the field of diagnostic imaging and patient care. With the necessary education and certification, individuals can embark on a fulfilling career that involves preparing and administering radioactive drugs, operating imaging equipment, and working closely with physicians to diagnose and treat medical conditions. The demand for nuclear medicine technologists is expected to grow, providing ample career opportunities in this field.
Also Read : Transform Your Medical Education With A Comprehensive Medical Rotation Plan
FAQ
Q: What is a nuclear medicine technologist?
A: A nuclear medicine technologist is a healthcare professional who prepares and administers radioactive drugs for imaging and therapeutic purposes, as well as explaining the procedures to patients and ensuring their safety during the process.
Q: What is the average salary of a nuclear medicine technologist in 2022?
A: The median annual salary for a nuclear medicine technologist in 2022 was $78,202, according to data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
Q: What are the job outlook and employment prospects for nuclear medicine technologists?
A: The employment of nuclear medicine technologists is projected to grow 8% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations. There will be a steady number of job openings for nuclear medicine technologists due to the increasing need for diagnostic imaging.
Q: What education and training are required to become a nuclear medicine technologist?
A: To become a nuclear medicine technologist, you’ll need to complete an accredited nuclear medicine program and obtain a degree from an accredited institution. Employers typically require certification, and some states may also require licensure.
Q: What does a nuclear medicine technologist do on the job?
A: Nuclear medicine technologists perform various duties, such as preparing and administering radioactive drugs, operating imaging equipment, and explaining procedures to patients. They work in settings like hospitals, diagnostic laboratories, and physicians’ offices under the supervision of physicians or other medical personnel.
Q: Is certification and licensing necessary to work as a nuclear medicine technologist?
A: Yes, many employers require certification, and some states may require licensing for nuclear medicine technologists. It is essential to check with your state’s health board for specific requirements.
Q: What is the median annual nuclear medicine technologist salary?
A: The median annual salary for nuclear medicine technologists in 2022 was $78,202, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Q: Is there a career growth potential for nuclear medicine technologists?
A: Yes, the job outlook for nuclear medicine technologists is positive, with a projected 8% growth in employment from 2022 to 2032, creating opportunities for individuals interested in this field.
Q: How is the use of nuclear medicine different from other imaging technologies like x-ray or computed tomography?
A: Unlike x-ray or computed tomography, which use external radiation to produce images, nuclear medicine involves the administration of radioactive drugs to the patient, which are then detected by imaging equipment to produce internal images of the body’s organs and tissues.
Q: Are there any specific requirements to work as a nuclear medicine technologist in the U.S.?
A: In the U.S., you’ll need to complete a degree program from an accredited institution and obtain certification to work as a nuclear medicine technologist. Some states may also require licensure, so it’s important to be aware of the specific requirements in your state.